FPGA SPI Bridge Panel(1)Arduinoスケッチ
2018/08/05 追記:OLEDモジュールを接続しない場合は、SSD1306Wire.h関連のコードを削除したスケッチを使ってください。
2018/06/09 追記:OLEDモジュールにIPアドレスを表示するようにしました。OLEDモジュールを接続しなくてもスケッチを変更する必要はありません。
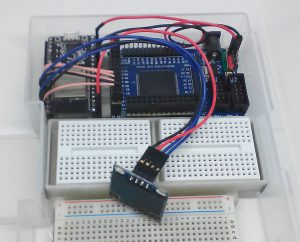
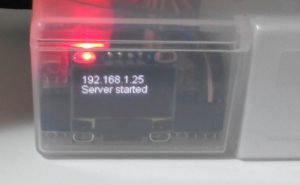
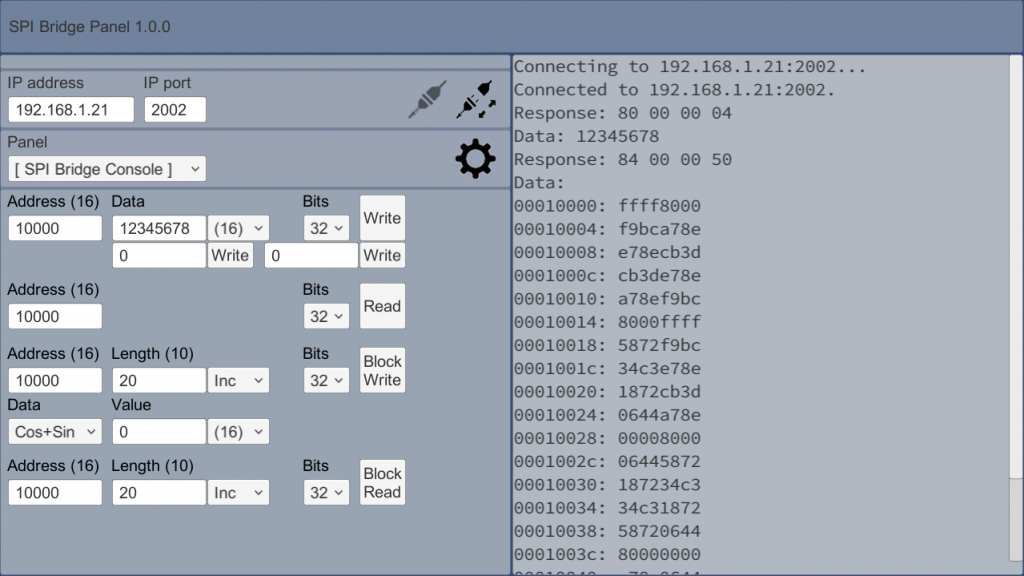
Google Playに「GUI Maker for Avalon Bus – FPGA SPI Bridge Panel」を公開しました。
「GUI Maker for ESP8266 & ESP32 – Python Inst. Panel」に「FPGA SPI Bridge Console for Avalon Bus」の機能を追加したものです。アンドロイド端末からFPGAを操作するGUIを短時間で作成できます。
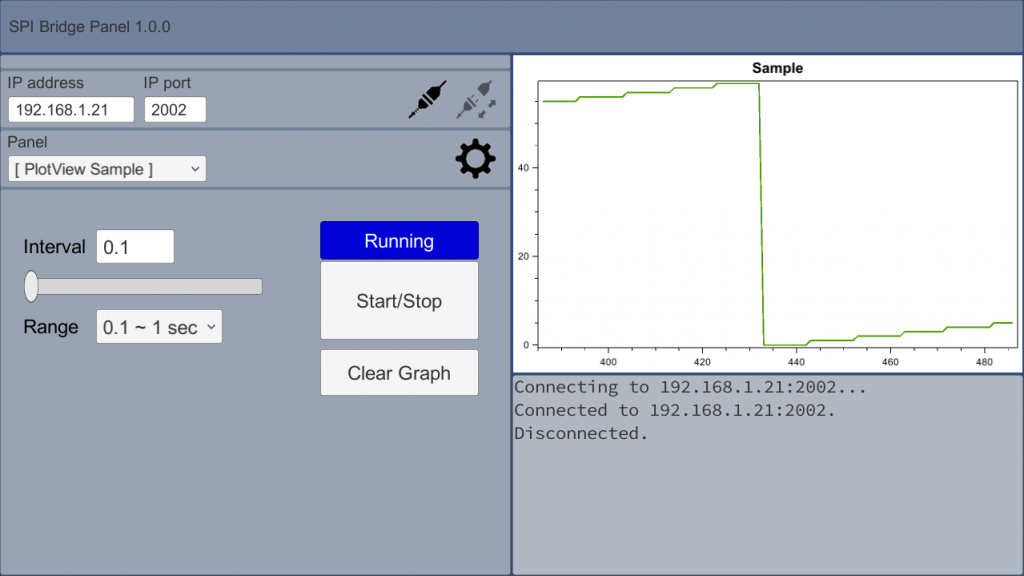
「GUI Maker for ESP8266 & ESP32 – Python Inst. Panel」と同様にグラフ付きのGUIも作れます。
Google Playの説明文をこちらにも載せておきます。
Qsysのオンライン・マニュアル「Embedded Peripheral IP User Guide」の「SPI Slave/JTAG to Avalon Master Bridge Cores」に書かれているように、JTAG以外にSPIでも外部からFPGA内部を操作できます。 Arduino、Raspberry PiなどからSPI経由でFPGAに実装した回路をアクセスできるのです。Nios II CPUを組み込まなくてもいいんです。 例えば、ESP-WROOM-32をWifiーSPI変換器として使えばアンドロイド端末からWifi経由でFPGAを操作できてしまいます。 アンドロイド端末 →(Wifi)→ ESP-WROOM-32 →(SPI)→ FPGA このアプリは「Python Inst. Panel - GUI maker for ESP8266 & ESP32」と同様に、ボタン、タイマー、グラフ等を貼り付けて処理をPythonで記述することで、FPGA用の操作パネルを簡単に作ることができます。 GUI関連は「Python Inst. Panel - GUI maker for ESP8266 & ESP32」の説明文とこのアプリに入っている「SPI Bridge Console」と「PlotView Sample」のPythonスクリプトを見てください。 Pythonスクリプトの中で次のメソッドを使ってFPGA内のAvalonバスをアクセスします。 byte[] WriteBytePacket(UInt32 addr, byte data, int timeoutInSec) byte[] WriteUInt16Packet(UInt32 addr, UInt16 data, int timeoutInSec) byte[] WriteUInt32Packet(UInt32 addr, UInt32 data, int timeoutInSec) byte[] WriteBytePacket(UInt32 addr, byte[] dataBytes, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec) byte[] WriteUInt16Packet(UInt32 addr, UInt16[] dataArray, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec) byte[] WriteUInt32Packet(UInt32 addr, UInt32[] dataArray, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec) byte ReadBytePacket(UInt32 addr, int timeoutInSec) UInt16 ReadUInt16Packet(UInt32 addr, int timeoutInSec) UInt32 ReadUInt32Packet(UInt32 addr, int timeoutInSec) byte[] ReadBytePacket(UInt16 size, UInt32 addr, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec) UInt16[] ReadUInt16Packet(UInt16 size, UInt32 addr, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec) UInt32[] ReadUInt32Packet(UInt16 size, UInt32 addr, bool isIncremental, int timeoutInSec)
以下は、ESP-WROOM-32用のOLEDありのスケッチです。
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SSD1306Wire.h"
/* Set these to your desired credentials. */
//const char *ssid = "ESPap";
//const char *password = "thereisnospoon";
const char* ssid = "your-ssid";
const char* password = "your-password";
WiFiServer server(2002);
WiFiClient client;
#define SPI_BUF_LEN 1024
byte spiBuf[SPI_BUF_LEN];
byte spiReadBuf[SPI_BUF_LEN];
SSD1306Wire display(0x3c, 21, 22);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
SPI.begin();
SPI.setFrequency(24000000);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE1);
SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST);
pinMode(SS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// Serial.println();
// Serial.print("Configuring access point...");
// /* You can remove the password parameter if you want the AP to be open. */
// WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP);
// WiFi.softAP(ssid, password);
// IPAddress myIP = WiFi.softAPIP();
// Serial.print("AP IP address: ");
// Serial.println(myIP);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
//WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); // Disable Access Point
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server started");
display.init();
display.flipScreenVertically();
display.setFont(ArialMT_Plain_16);
display.drawString(0, 0, WiFi.localIP().toString());
display.drawString(0, 16, "Server started");
display.display();
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
// try to connect to a new client
client = server.available();
} else {
// read data from the connected client
int n = client.available();
if (n > 0) {
//Serial.print("available: ");
//Serial.println(n);
if (n > SPI_BUF_LEN) {
n = SPI_BUF_LEN;
}
// transfer data to/from SPI
client.readBytes(spiBuf, n);
digitalWrite(SS, LOW);
SPI.transferBytes(spiBuf, spiReadBuf, n);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// return data to client
client.write(spiReadBuf, n);
}
}
}
以下は、ESP-WROOM-32用のOLED無しのスケッチです。
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <Wire.h>
/* Set these to your desired credentials. */
//const char *ssid = "ESPap";
//const char *password = "thereisnospoon";
const char* ssid = "106F3F28087C_G";
const char* password = "xr84vyms434wt";
WiFiServer server(2002);
WiFiClient client;
#define SPI_BUF_LEN 1024
byte spiBuf[SPI_BUF_LEN];
byte spiReadBuf[SPI_BUF_LEN];
void printBytes(byte *bytes, int bytesSize);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
SPI.begin();
SPI.setFrequency(24000000);
SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE1);
SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST);
pinMode(SS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// Serial.println();
// Serial.print("Configuring access point...");
// /* You can remove the password parameter if you want the AP to be open. */
// WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP);
// WiFi.softAP(ssid, password);
// IPAddress myIP = WiFi.softAPIP();
// Serial.print("AP IP address: ");
// Serial.println(myIP);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
//WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); // Disable Access Point
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server started");
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
// try to connect to a new client
client = server.available();
} else {
// read data from the connected client
int n = client.available();
if (n > 0) {
//Serial.print("available: ");
//Serial.println(n);
if (n > SPI_BUF_LEN) {
n = SPI_BUF_LEN;
}
// transfer data to/from SPI
client.readBytes(spiBuf, n);
//printBytes(spiBuf, n);
digitalWrite(SS, LOW);
SPI.transferBytes(spiBuf, spiReadBuf, n);
digitalWrite(SS, HIGH);
// return data to client
//printBytes(spiReadBuf, n);
client.write(spiReadBuf, n);
}
}
}
void printBytes(byte *bytes, int bytesSize) {
Serial.println();
for (int i = 0; i < bytesSize; i++) {
Serial.print(bytes[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
}